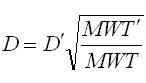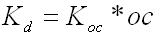Copyright © 2023 ESCI, LLC - All Rights Reserved.
AT123D Aquifer and Chemical Input
Parameters
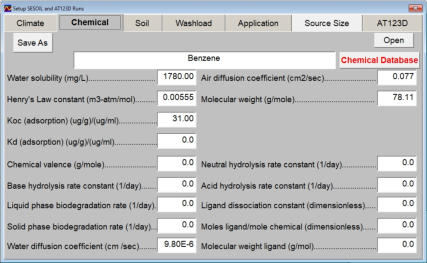
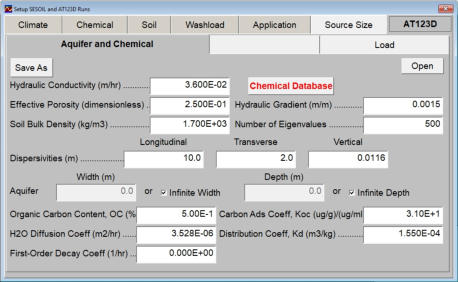
The aquifer and chemical input tab contains information on the physical properties of the aquifer and contaminants. These properties are used by AT123D to predict the transport and fate of contaminants in groundwater. As SEVIEW contains a chemical database for the most part all you need to do is find your chemical. Properties for additional contaminants can be found on the internet or in various references. A detailed description of each input parameter is provided below. Additional information on these parameters can be found in the SEVIEW help file and User's Guide. Hydraulic Conductivity The horizontal hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer. Determined from pump tests, slug tests, or estimated based on the aquifer soil type. Hydraulic Gradient The slope of the water table. Determined from potentiometric surface maps of the static water level data from monitoring wells. Effective Porosity Effective porosity is the fraction of interconnected pore space to the total volume of the soil. This parameter is difficult to measure and is typically estimated based on aquifer soil type. Default values can be found in the SEVIEW User’s Guide and help documentation. Bulk Density Bulk density is the amount of mass per unit volume of the aquifer. Number of Eigenvalues The number of eigenvalues establishes the maximum number of terms that will be calculated for a series solution before truncation occurs. Dispersivities The process whereby a contaminant plume spreads out due to mechanical mixing in the aquifer. See the SEVIEW User’s Guide to learn how to estimate values for this parameter. Aquifer Dimensions AT123D simulates both confined and unconfined aquifers. Water Diffusion Coefficient Diffusion consists of the random motion of atoms or molecules in a gas or liquid. This motion causes contaminants to disperse from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. Diffusion is controlled by molecular weight, in that lighter atoms or molecules are dispersed at higher rates. This dependency on weight can be used to establish diffusion coefficients for additional chemicals using the equation below: Where D =Diffusion coefficient of the current molecule in cm 2 /sec D’ = Diffusion coefficient for a reference molecule in cm 2 /sec MWT′ = Molecular weight of the reference molecule in g/mole MWT = Molecular weight of the current molecule in g/mole This equation can be used to estimate both air and water diffusion coefficients. Please note that almost any substance can be used as the reference molecule. Organic Carbon Content The organic carbon content is defined as the percent of organic carbon of the aquifer soil. This is one of the most important site-specific parameters and care should be taken as to which analytical method should be used. Carbon Adsorption Coefficient (Koc) The organic carbon adsorption coefficient (K oc ) is the chemical adsorption coefficient normalized to the organic carbon content of the soil in (µg/g)/(µg/ml). This parameter establishes the tendency of a substance to bind to organic matter in the aquifer. Distribution Coefficient (Kd) The Kd value can be directly entered if non-zero values for Koc and soil organic carbon content are entered. If values for both Koc and soil organic carbon content are entered AT123D calculates the soil partition coefficient (Kd) using the following equation. Where K d = Soil partition coefficient in (µg/g)/(µg/ml) K oc = Organic carbon adsorption coefficient in (µg/g)/(µg/ml) oc = Fraction soil organic carbon content First-Order Decay Coefficient (Biodegradation) Biodegradation is the process by which a chemical is converted to a new form via biotic reactions. AT123D simulates biodegradation as a first-order decay process.
SEVIEW
Transport and fate modeling software
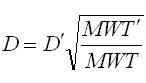
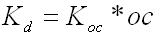

AT123D Aquifer and
Chemical Input
Parameters
The aquifer and chemical input tab contains information on the physical properties of the aquifer and contaminants. These properties are used by AT123D to predict the transport and fate of contaminants in groundwater. As SEVIEW contains a chemical database for the most part all you need to do is find your chemical. Properties for additional contaminants can be found on the internet or in various references. A detailed description of each input parameter is provided below. Additional information on these parameters can be found in the SEVIEW help file and User's Guide. Hydraulic Conductivity The horizontal hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer. Determined from pump tests, slug tests, or estimated based on the aquifer soil type. Hydraulic Gradient The slope of the water table. Determined from potentiometric surface maps of the static water level data from monitoring wells. Effective Porosity Effective porosity is the fraction of interconnected pore space to the total volume of the soil. This parameter is difficult to measure and is typically estimated based on aquifer soil type. Default values can be found in the SEVIEW User’s Guide and help documentation. Bulk Density Bulk density is the amount of mass per unit volume of the aquifer. Number of Eigenvalues The number of eigenvalues establishes the maximum number of terms that will be calculated for a series solution before truncation occurs. Dispersivities The process whereby a contaminant plume spreads out due to mechanical mixing in the aquifer. See the SEVIEW User’s Guide to learn how to estimate values for this parameter. Aquifer Dimensions AT123D simulates both confined and unconfined aquifers. Water Diffusion Coefficient Diffusion consists of the random motion of atoms or molecules in a gas or liquid. This motion causes contaminants to disperse from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. Diffusion is controlled by molecular weight, in that lighter atoms or molecules are dispersed at higher rates. This dependency on weight can be used to establish diffusion coefficients for additional chemicals using the equation below: Where D =Diffusion coefficient of the current molecule in cm 2 /sec D’ = Diffusion coefficient for a reference molecule in cm 2 /sec MWT′ = Molecular weight of the reference molecule in g/mole MWT = Molecular weight of the current molecule in g/mole This equation can be used to estimate both air and water diffusion coefficients. Please note that almost any substance can be used as the reference molecule. Organic Carbon Content The organic carbon content is defined as the percent of organic carbon of the aquifer soil. This is one of the most important site-specific parameters and care should be taken as to which analytical method should be used. Carbon Adsorption Coefficient (Koc) The organic carbon adsorption coefficient (K oc ) is the chemical adsorption coefficient normalized to the organic carbon content of the soil in (µg/g)/(µg/ml). This parameter establishes the tendency of a substance to bind to organic matter in the aquifer. Distribution Coefficient (Kd) The Kd value can be directly entered if non-zero values for Koc and soil organic carbon content are entered. If values for both Koc and soil organic carbon content are entered AT123D calculates the soil partition coefficient (Kd) using the following equation. Where K d = Soil partition coefficient in (µg/g)/(µg/ml) K oc = Organic carbon adsorption coefficient in (µg/g)/(µg/ml) oc = Fraction soil organic carbon content First-Order Decay Coefficient (Biodegradation) Biodegradation is the process by which a chemical is converted to a new form via biotic reactions. AT123D simulates biodegradation as a first-order decay process.
SEVIEW
Transport and fate modeling software